Ambien side effects are a common concern for individuals prescribed this sleep medication. While Ambien is effective in treating insomnia, it’s crucial to understand the potential risks associated with its use. From drowsiness and dizziness to more serious side effects, navigating the complexities of Ambien requires a comprehensive understanding of its impact on the body.
This guide delves into the various side effects of Ambien, ranging from the most common to the potentially serious. We’ll explore the mechanism of action, interactions with other medications, and the potential for dependence and withdrawal. Additionally, we’ll discuss the risks of driving and consuming alcohol while taking Ambien, as well as its effects during pregnancy and breastfeeding. By shedding light on these aspects, we aim to empower individuals to make informed decisions about their health and well-being.
Ambien’s Mechanism of Action
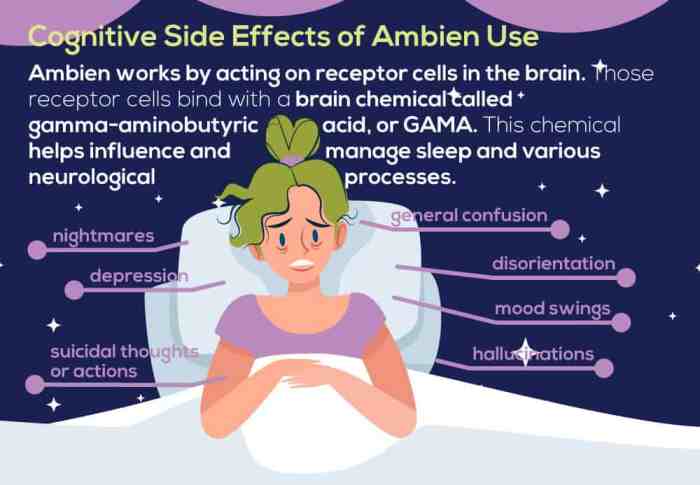
Ambien, also known as Zolpidem, is a hypnotic medication commonly prescribed for insomnia. It works by enhancing the effects of a neurotransmitter called GABA in the brain. GABA, or gamma-aminobutyric acid, is an inhibitory neurotransmitter, meaning it helps calm the brain and induce sleep.
How Ambien Works
Ambien’s mechanism of action involves its interaction with specific receptors in the brain. It primarily targets the GABAA receptor, a protein complex found in nerve cells. When Ambien binds to the GABAA receptor, it enhances the effects of GABA, increasing its inhibitory activity. This results in a calming effect on the brain, promoting sleepiness and reducing wakefulness.
Neurotransmitters and Receptors Involved
- GABA (Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid): The primary neurotransmitter targeted by Ambien. GABA is an inhibitory neurotransmitter that helps regulate brain activity, promoting relaxation and sleep.
- GABAA Receptor: A protein complex found in nerve cells that binds to GABA. Ambien binds to this receptor, enhancing the effects of GABA and promoting sleepiness.
Comparison to Other Sleep Medications
Ambien’s mechanism of action differs from other sleep medications, such as benzodiazepines. While both Ambien and benzodiazepines target the GABAA receptor, Ambien has a higher affinity for a specific subtype of the receptor, known as the alpha-1 subunit. This difference in affinity contributes to Ambien’s shorter duration of action compared to benzodiazepines.
Common Side Effects
Ambien, like many medications, can cause side effects. These effects can vary in severity and frequency from person to person. It’s important to understand the potential side effects so you can discuss them with your doctor and manage them if they occur.
Drowsiness and Sedation
Drowsiness is one of the most common side effects of Ambien. This is because Ambien is a sedative-hypnotic medication, meaning it slows down the central nervous system, which can lead to feelings of drowsiness and sleepiness.
This drowsiness can last into the morning after taking Ambien, especially if you take it too close to bedtime.
It’s important to avoid driving or operating machinery after taking Ambien, as this can be dangerous.
Dizziness and Lightheadedness
Dizziness and lightheadedness are also common side effects of Ambien. These side effects are usually mild and tend to go away after a few days of taking the medication. However, if you experience severe dizziness or lightheadedness, you should contact your doctor.
Memory Problems
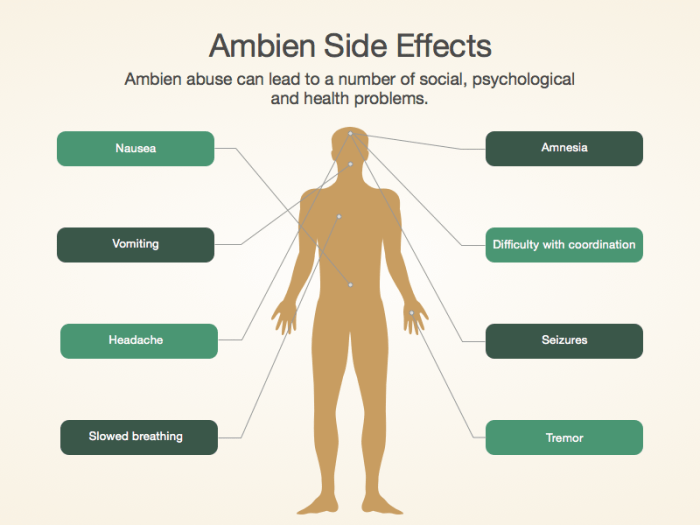
Ambien can also cause memory problems, such as amnesia. This is because Ambien affects the part of the brain that is responsible for memory.
These memory problems can include forgetting events that happened while you were taking Ambien, or even forgetting to take the medication itself.
In some cases, people have reported engaging in activities while they were asleep, such as driving or eating, and not remembering it the next day.
If you experience memory problems while taking Ambien, it’s important to talk to your doctor.
Other Side Effects
In addition to drowsiness, dizziness, and memory problems, other common side effects of Ambien include:
- Headache
- Nausea
- Dry mouth
- Constipation
- Muscle weakness
- Blurred vision
- Changes in taste
- Skin rash
Serious Side Effects: Ambien Side Effects
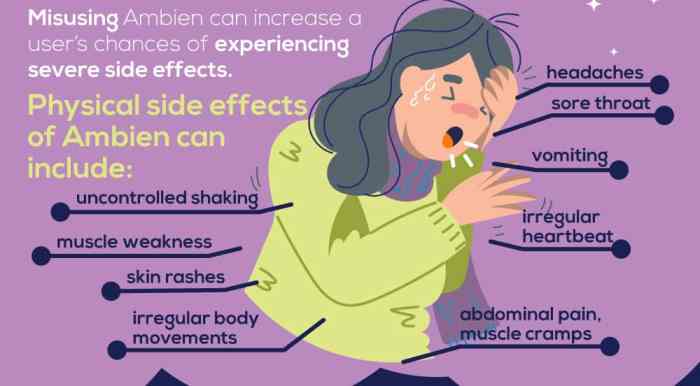
While Ambien is generally safe for most people when used as prescribed, it can cause serious side effects in some individuals. These side effects can be severe and even life-threatening, so it’s important to be aware of the risks and to talk to your doctor if you experience any concerning symptoms.
Risk Factors for Serious Side Effects
Several factors can increase the risk of experiencing serious side effects from Ambien, including:
- Age: Older adults are more likely to experience side effects from Ambien, including confusion, dizziness, and falls.
- Medical conditions: People with certain medical conditions, such as liver or kidney disease, may be more likely to experience side effects from Ambien.
- Other medications: Ambien can interact with other medications, increasing the risk of side effects. It’s important to tell your doctor about all the medications you’re taking, including over-the-counter drugs and herbal supplements.
- Alcohol use: Combining Ambien with alcohol can significantly increase the risk of serious side effects, including drowsiness, dizziness, and impaired coordination.
- Drug abuse: Misusing Ambien, such as taking more than the prescribed dose or using it for recreational purposes, can lead to serious side effects, including overdose.
Types of Serious Side Effects
The following are some of the most serious side effects that can occur with Ambien use:
- Allergic reactions: Ambien can cause allergic reactions, which can range from mild skin rash to life-threatening anaphylaxis. Symptoms of an allergic reaction can include hives, itching, swelling, difficulty breathing, and a rapid heartbeat. If you experience any of these symptoms, seek medical attention immediately.
- Sleepwalking and other sleep-related behaviors: Ambien can cause sleepwalking, sleep-driving, and other sleep-related behaviors that can be dangerous. These behaviors can occur even if you don’t remember taking the medication. It’s important to take Ambien only in a safe environment and to avoid driving or operating machinery after taking it.
- Dependence and addiction: Ambien can be habit-forming, and some people may develop dependence or addiction to the drug. This can lead to withdrawal symptoms when you stop taking the medication, which can be uncomfortable and even dangerous. It’s important to talk to your doctor about the risks of dependence and addiction before taking Ambien.
- Overdose: Taking too much Ambien can lead to overdose, which can be fatal. Symptoms of Ambien overdose can include drowsiness, confusion, dizziness, slurred speech, slowed breathing, and coma. If you suspect someone has overdosed on Ambien, call 911 immediately.
Consequences of Serious Side Effects
Serious side effects from Ambien can have a significant impact on your health and well-being. They can lead to:
- Injuries: Sleepwalking, sleep-driving, and other sleep-related behaviors can lead to injuries, including falls, car accidents, and other accidents.
- Legal problems: Sleep-driving can lead to legal problems, such as driving under the influence charges.
- Relationship problems: Dependence and addiction to Ambien can lead to relationship problems, as well as financial problems.
- Death: Overdose on Ambien can be fatal.
Interactions with Other Medications
Ambien, like many medications, can interact with other drugs, potentially leading to adverse effects. These interactions can occur when Ambien is taken with certain medications, including over-the-counter drugs, supplements, and alcohol. It is crucial to inform your doctor about all the medications you are taking, including herbal supplements and over-the-counter drugs, before starting Ambien therapy.
Interactions with Other Medications
It is essential to understand the potential interactions of Ambien with other medications. Ambien can interact with various drugs, including:
- Central Nervous System (CNS) depressants: This category includes medications that slow down brain activity, such as benzodiazepines (e.g., diazepam, alprazolam), opioids (e.g., morphine, oxycodone), and alcohol. Combining Ambien with these drugs can increase the risk of drowsiness, dizziness, slowed breathing, and even coma.
- Antibiotics: Certain antibiotics, like erythromycin and clarithromycin, can increase the levels of Ambien in the body, leading to prolonged sleepiness and increased side effects.
- Antidepressants: Some antidepressants, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) like fluoxetine and paroxetine, can interact with Ambien, potentially increasing the risk of serotonin syndrome, a potentially life-threatening condition characterized by confusion, agitation, and muscle rigidity.
- Antihistamines: Over-the-counter antihistamines like diphenhydramine (Benadryl) can also increase drowsiness when combined with Ambien.
- Certain antifungals: Medications like ketoconazole can increase the levels of Ambien in the body, leading to enhanced sedative effects.
Examples of Specific Interactions
- Ambien and Alcohol: Combining Ambien with alcohol can significantly enhance the sedative effects of both drugs, leading to severe drowsiness, dizziness, and impaired coordination. In extreme cases, this combination can even lead to respiratory depression and coma.
- Ambien and Benzodiazepines: Using Ambien with benzodiazepines, such as diazepam (Valium) or alprazolam (Xanax), can significantly increase the risk of sedation, respiratory depression, and impaired cognitive function. This combination can be particularly dangerous for older adults and those with respiratory problems.
- Ambien and Opioids: Combining Ambien with opioids, such as morphine or oxycodone, can lead to a synergistic effect, causing extreme drowsiness, slowed breathing, and even death. This combination is highly dangerous and should be avoided.
Dependence and Withdrawal
Ambien, like other benzodiazepines, can lead to dependence with prolonged use. This means your body can become accustomed to the drug and require higher doses to achieve the same effect. It’s important to understand the potential for dependence and withdrawal symptoms before starting Ambien.
Ambien Dependence
Dependence on Ambien can occur even with short-term use, although the risk increases with prolonged use and high doses. Individuals with a history of substance abuse are at higher risk of developing dependence. The risk of dependence is also higher for those who use Ambien for recreational purposes.
Ambien Withdrawal, Ambien side effects
Withdrawal symptoms can occur when you stop taking Ambien abruptly or reduce your dose too quickly. These symptoms can range from mild to severe and may include:
* Insomnia: Difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep.
* Anxiety: Feeling restless, nervous, or agitated.
* Irritability: Feeling easily frustrated or upset.
* Headaches: Pain in the head.
* Muscle aches: Pain in the muscles.
* Sweating: Excessive sweating.
* Nausea: Feeling sick to your stomach.
* Seizures: In severe cases, Ambien withdrawal can lead to seizures.
Discontinuing Ambien Use
If you are taking Ambien and want to stop, it’s important to do so gradually under the guidance of your doctor. Abruptly stopping Ambien can increase the risk of withdrawal symptoms. Your doctor can help you taper off the medication safely.
Ambien and Driving
Driving under the influence of Ambien is extremely dangerous and should be strictly avoided. Ambien can significantly impair your judgment, reaction time, and coordination, making it unsafe to operate a vehicle.
Effects of Ambien on Driving
Ambien’s effects on cognitive function and motor skills can significantly impair driving abilities. These effects can include:
- Drowsiness and sleepiness: This is the most common side effect of Ambien and can make it difficult to stay awake and alert while driving.
- Slowed reaction time: Ambien can delay your reaction time, making it difficult to respond quickly to unexpected situations on the road.
- Impaired coordination: Ambien can affect your coordination and make it difficult to control your vehicle.
- Confusion and disorientation: Ambien can cause confusion and disorientation, making it difficult to make sound judgments while driving.
- Memory problems: Ambien can impair your memory, making it difficult to remember where you are going or what you are doing.
- Visual disturbances: Ambien can cause blurred vision or double vision, which can make it difficult to see clearly while driving.
Ambien and Alcohol
Combining Ambien with alcohol is extremely dangerous and can have severe consequences. Both Ambien and alcohol are central nervous system depressants, meaning they slow down brain activity. When taken together, their effects are amplified, leading to a potentially life-threatening situation.
Synergistic Effects
When Ambien and alcohol are combined, their effects are synergistic, meaning they work together to produce a greater effect than either substance alone. This can lead to:
- Excessive drowsiness and sedation
- Impaired coordination and balance
- Slurred speech
- Slowed breathing
- Loss of consciousness
- Coma
- Death
Warnings
It is crucial to understand the potential risks associated with mixing Ambien and alcohol. Here are some warnings to consider:
- Never drink alcohol while taking Ambien.
- Avoid consuming alcohol for at least several hours before and after taking Ambien.
- Be cautious about taking Ambien if you have a history of alcohol abuse or dependence.
- If you experience any unusual or severe side effects after combining Ambien and alcohol, seek immediate medical attention.
Ambien and Pregnancy
Ambien is a sedative-hypnotic medication used to treat insomnia. It is crucial to understand the potential risks associated with using Ambien during pregnancy. While Ambien can be effective for treating insomnia, it is important to weigh the potential benefits against the potential risks to both the mother and the developing fetus.
Potential Risks of Ambien Use During Pregnancy
Using Ambien during pregnancy can pose potential risks to both the mother and the developing fetus. It is important to discuss the risks and benefits of Ambien use with your doctor before taking it.
- Increased risk of birth defects: Some studies have suggested a possible association between Ambien use during pregnancy and an increased risk of birth defects. These defects may include cleft palate, heart defects, and other abnormalities.
- Premature birth: Ambien use during pregnancy may increase the risk of premature birth. Premature babies often have health problems that can require extra care and monitoring.
- Low birth weight: Babies born to mothers who used Ambien during pregnancy may have a lower birth weight. Low birth weight can lead to various health issues.
- Withdrawal symptoms in the newborn: Babies born to mothers who have been taking Ambien regularly may experience withdrawal symptoms after birth. These symptoms can include tremors, irritability, and feeding difficulties.
Ambien and Breastfeeding
Ambien (zolpidem) is a medication used to treat insomnia. It’s a sedative-hypnotic drug that works by slowing down the central nervous system. While Ambien is generally effective in treating insomnia, it’s important to consider its potential risks when breastfeeding.
The use of Ambien during breastfeeding is a concern because the drug can pass into breast milk. This means that the baby could be exposed to Ambien, which could potentially lead to adverse effects.
Ambien Transfer into Breast Milk
Ambien is known to transfer into breast milk, and the amount that passes into breast milk is dependent on the mother’s dose and the time since she took the medication. Studies have shown that Ambien is detectable in breast milk for up to 24 hours after a single dose. The amount of Ambien in breast milk typically peaks around 2 to 4 hours after taking the medication.
Recommendations for Breastfeeding Mothers
If you are breastfeeding and considering taking Ambien, it’s crucial to discuss the risks and benefits with your doctor. They can help you weigh the potential risks to your baby against the benefits of Ambien for you.
Here are some recommendations for breastfeeding mothers considering Ambien use:
- Discuss your options with your doctor. They can help you weigh the potential risks to your baby against the benefits of Ambien for you. They may also recommend alternative treatments for insomnia that are safer for breastfeeding mothers.
- Avoid breastfeeding for at least 4 hours after taking Ambien. This allows the medication to be eliminated from your body and reduces the amount of Ambien that could pass into breast milk.
- Pump and discard breast milk for at least 4 hours after taking Ambien. This is another way to reduce your baby’s exposure to Ambien.
- Monitor your baby for any side effects. If you notice any unusual behavior or symptoms in your baby, contact your doctor immediately.
It’s essential to understand that the decision to use Ambien while breastfeeding is a personal one. Weigh the potential risks and benefits with your doctor and make the best decision for you and your baby.
Long-Term Effects
While Ambien is generally safe for short-term use, prolonged use can lead to potential long-term effects. It’s crucial to understand these effects and discuss them with your doctor to ensure you’re using Ambien safely and effectively.
Impact on Brain Function
Prolonged Ambien use can have a significant impact on brain function. The drug’s effects on the central nervous system can lead to changes in brain chemistry and function, potentially impacting cognitive abilities and sleep patterns.
Long-Term Risks and Benefits
Long-term Ambien use can pose both risks and benefits. It’s important to weigh these carefully and discuss them with your doctor.
- Risks:
- Tolerance: Over time, your body may develop a tolerance to Ambien, requiring higher doses for the same effect. This can increase the risk of side effects and dependence.
- Dependence: Prolonged Ambien use can lead to dependence, meaning you may experience withdrawal symptoms if you stop taking it abruptly. These symptoms can include insomnia, anxiety, and seizures.
- Cognitive Impairment: Long-term use may lead to cognitive impairment, affecting memory, concentration, and decision-making.
- Sleep Disorders: Paradoxically, prolonged Ambien use can worsen sleep disorders, leading to rebound insomnia or dependence on the drug to sleep.
- Increased Risk of Falls and Accidents: Ambien can impair coordination and balance, increasing the risk of falls and accidents, especially in older adults.
- Mental Health Issues: In some cases, long-term Ambien use may be linked to an increased risk of depression, anxiety, and other mental health problems.
- Benefits:
- Improved Sleep Quality: For individuals with chronic insomnia, Ambien can provide significant relief, improving sleep quality and reducing daytime sleepiness.
- Reduced Anxiety: Ambien can help reduce anxiety and improve mood in some individuals, particularly those with anxiety disorders.
It’s crucial to remember that Ambien is a powerful medication and should only be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Understanding the potential side effects of Ambien is crucial for making informed decisions about its use. While it can be a valuable tool for managing insomnia, it’s essential to weigh the benefits against the risks. By carefully considering your individual needs and circumstances, you can work with your healthcare provider to determine if Ambien is the right choice for you. Remember, open communication with your doctor is vital in ensuring your safety and maximizing the benefits of any medication you take.
While Ambien is known for its sleep-inducing properties, it can also come with a range of side effects, including dizziness, drowsiness, and confusion. These side effects can be particularly concerning for individuals taking medications like pembrolizumab , which can also cause fatigue and confusion. It’s crucial to discuss any potential drug interactions with your doctor, ensuring that the benefits of Ambien outweigh the potential risks.