Aducanumab, a groundbreaking monoclonal antibody, has emerged as a beacon of hope in the relentless battle against Alzheimer’s disease. This revolutionary treatment targets amyloid beta plaques, the hallmark of the debilitating neurodegenerative condition, offering a potential avenue for slowing cognitive decline and improving quality of life for patients.
The development of aducanumab has been a long and arduous journey, marked by extensive research, clinical trials, and intense scrutiny from regulatory bodies. Its approval by the FDA in 2021 sparked a wave of controversy, with some experts praising its potential while others expressed concerns about its efficacy and safety. Despite the debate, aducanumab represents a significant step forward in Alzheimer’s research, offering a glimpse into a future where this devastating disease might be effectively managed.
Aducanumab: Future Directions and Research
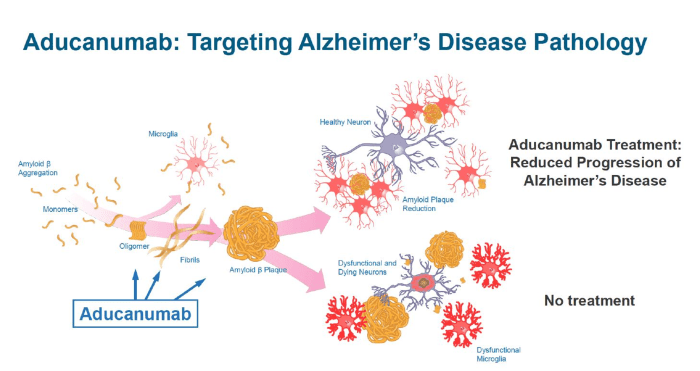
Aducanumab, the first FDA-approved treatment for Alzheimer’s disease in over two decades, represents a significant milestone in the fight against this devastating disease. While its approval sparked debate, ongoing research continues to explore its potential and address unanswered questions.
Ongoing Research and Potential Applications
The potential of aducanumab extends beyond treating Alzheimer’s disease. Research is actively exploring its efficacy in other neurological conditions, including:
- Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI): Studies are investigating if aducanumab can prevent or delay the progression of MCI to Alzheimer’s disease. This research aims to identify individuals at high risk of developing Alzheimer’s and intervene early to potentially slow or halt the disease process.
- Other Neurodegenerative Diseases: Researchers are exploring whether aducanumab could be effective in treating other neurodegenerative diseases characterized by amyloid plaques, such as Parkinson’s disease and Lewy body dementia. This research could potentially broaden the therapeutic applications of aducanumab.
Combination Therapies for Enhanced Efficacy, Aducanumab
Combining aducanumab with other treatments for Alzheimer’s disease is a promising area of research. This approach aims to enhance the therapeutic effects by targeting different aspects of the disease process. Some potential combination therapies include:
- Cholinesterase Inhibitors: Combining aducanumab with cholinesterase inhibitors, such as donepezil, rivastigmine, and galantamine, could potentially improve cognitive function and slow disease progression. Cholinesterase inhibitors work by increasing the levels of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter involved in memory and learning, which may complement aducanumab’s amyloid-clearing action.
- NMDA Receptor Antagonists: Combining aducanumab with NMDA receptor antagonists, such as memantine, could potentially protect neurons from damage caused by excessive glutamate activity. This combination could potentially address the neurotoxicity associated with Alzheimer’s disease, further enhancing the therapeutic benefits.
Future Prospects and Disease Modification
The long-term clinical utility of aducanumab remains under investigation. However, the potential for disease modification is a significant aspect of its future prospects. While current evidence suggests aducanumab can slow cognitive decline, further research is needed to determine if it can truly modify the disease course and prevent or delay the onset of Alzheimer’s disease.
- Disease Modification: The ability to modify the disease course would be a major breakthrough in treating Alzheimer’s disease. This could involve slowing or halting the progression of the disease, potentially leading to improved quality of life and increased lifespan for patients.
- Long-Term Efficacy: Ongoing research is essential to determine the long-term efficacy and safety of aducanumab. Understanding the long-term effects of treatment is crucial for optimizing patient care and ensuring its long-term benefits outweigh potential risks.
Aducanumab and Patient Management
Aducanumab is a groundbreaking treatment for Alzheimer’s disease, offering hope for slowing cognitive decline. However, managing patients on this therapy requires a comprehensive approach, encompassing careful monitoring for potential side effects and adjustments in dosage.
Monitoring for Side Effects
It is crucial to monitor patients for potential side effects of aducanumab treatment. These side effects can vary in severity and frequency.
| Side Effect | Severity | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Amyloid-related imaging abnormalities (ARIA) | Mild to severe | Common |
| Headache | Mild to moderate | Common |
| Nausea | Mild to moderate | Less common |
| Dizziness | Mild to moderate | Less common |
| Brain swelling | Rare | Rare |
| Bleeding in the brain | Rare | Rare |
Adjusting Dosages
The dosage of aducanumab may need to be adjusted based on the individual patient’s response to treatment and the presence of any side effects. For instance, if a patient experiences ARIA, the dosage may be reduced or the treatment may be temporarily paused.
Patient Education and Support
Providing patients with comprehensive education about Alzheimer’s disease and its treatments is essential. This includes explaining the potential benefits and risks of aducanumab therapy, as well as the importance of ongoing monitoring.
“Patients should be informed about the potential side effects of aducanumab, such as ARIA, and how to recognize and report these symptoms.”
Moreover, providing patients with emotional support and resources can help them cope with the challenges of Alzheimer’s disease and its treatments. This may involve connecting them with support groups, counseling services, or other community resources.
Aducanumab: Societal and Ethical Considerations
Aducanumab’s introduction as a treatment for Alzheimer’s disease raises significant ethical and societal concerns. Its high cost, potential for overtreatment, and impact on healthcare systems necessitate careful consideration.
Ethical Considerations
The ethical considerations surrounding aducanumab are multifaceted and require a balanced approach.
- Cost: Aducanumab is a very expensive treatment, with annual costs estimated to be in the tens of thousands of dollars. This raises concerns about accessibility for patients, particularly those with limited financial resources. It also raises questions about the value of the treatment relative to its cost, especially considering the limited clinical evidence and potential for overtreatment.
- Accessibility: The high cost of aducanumab creates a significant barrier to access for many patients. This raises concerns about equity and fairness in healthcare, as those with financial resources may have preferential access to the treatment. It also highlights the need for robust insurance coverage and government programs to ensure equitable access.
- Overtreatment: Aducanumab’s approval was based on a controversial clinical trial, with some experts questioning the efficacy of the drug. This raises concerns about the potential for overtreatment, where patients may be subjected to unnecessary risks and side effects without receiving significant clinical benefit. It emphasizes the importance of careful patient selection and monitoring to ensure appropriate use of the drug.
Societal Impact
Aducanumab’s introduction has significant implications for healthcare systems and resource allocation.
- Cost Burden: The high cost of aducanumab could place a significant strain on healthcare systems, particularly in countries with limited resources. This could lead to reduced access to other essential healthcare services or necessitate difficult choices about resource allocation.
- Resource Allocation: The allocation of resources for aducanumab raises complex ethical considerations. Should scarce resources be directed towards a treatment with limited evidence and high cost, or towards other healthcare priorities? This debate requires careful consideration of the potential benefits and risks of aducanumab in relation to other healthcare needs.
Impact on Individuals and Families
Aducanumab’s potential benefits and risks have profound implications for individuals with Alzheimer’s disease and their families.
- Hope and Expectations: Aducanumab has generated hope for individuals with Alzheimer’s disease and their families, offering a potential treatment option that could slow disease progression. However, it’s crucial to manage expectations and acknowledge the limitations of the drug, ensuring that patients and families are fully informed about its potential benefits and risks.
- Quality of Life: The impact of aducanumab on quality of life for individuals with Alzheimer’s disease and their families is a complex issue. While the drug may offer some cognitive benefits, it can also come with significant side effects, including headaches, nausea, and brain swelling. It’s important to carefully assess the potential benefits and risks of the drug in relation to individual patient needs and preferences.
Aducanumab: A Case Study
This section will explore a hypothetical case study of a patient with Alzheimer’s disease who is being considered for aducanumab therapy. The case study will demonstrate the decision-making process involved in determining if aducanumab is appropriate for the patient, considering their individual needs and circumstances. Additionally, it will analyze the potential outcomes of aducanumab treatment for the patient, considering both benefits and risks.
Patient Profile and Decision-Making Process
This case study focuses on a 72-year-old woman named Mrs. Smith, who has been diagnosed with mild Alzheimer’s disease. She exhibits memory impairment, difficulty with language, and mild cognitive decline. Her family is seeking treatment options to slow down the progression of the disease and improve her quality of life.
The decision-making process for determining if aducanumab is appropriate for Mrs. Smith involves a comprehensive evaluation. This evaluation includes:
- Medical History and Physical Examination: A thorough assessment of Mrs. Smith’s medical history, including any pre-existing conditions, medications, and allergies, is crucial. A physical examination helps assess her overall health status and identify any potential risks associated with aducanumab treatment.
- Cognitive Assessment: A neuropsychological evaluation is conducted to assess Mrs. Smith’s cognitive function and determine the severity of her Alzheimer’s disease. This evaluation typically involves standardized tests that assess memory, language, attention, and executive function.
- Imaging Studies: Brain imaging studies, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or positron emission tomography (PET) scans, may be performed to confirm the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease and assess the presence of amyloid plaques in the brain. These plaques are the primary target of aducanumab.
- Risk-Benefit Assessment: A careful consideration of the potential benefits and risks of aducanumab treatment is essential. The benefits of aducanumab include the potential to slow down the progression of Alzheimer’s disease and improve cognitive function. However, the risks include potential side effects such as amyloid-related imaging abnormalities (ARIA), which can cause swelling or bleeding in the brain.
- Patient Preferences and Goals: It is crucial to involve Mrs. Smith and her family in the decision-making process. Their preferences and goals regarding treatment should be carefully considered. They need to understand the potential benefits and risks of aducanumab therapy and make an informed decision based on their individual needs and values.
Potential Outcomes of Aducanumab Treatment
Based on the evaluation, the healthcare team determines that Mrs. Smith is a suitable candidate for aducanumab therapy. The potential outcomes of treatment for Mrs. Smith are:
- Potential Benefits: Aducanumab may help slow down the progression of Alzheimer’s disease in Mrs. Smith, potentially delaying the onset of more severe symptoms and improving her quality of life. The drug could potentially reduce the accumulation of amyloid plaques in her brain, leading to improved cognitive function and a slower rate of cognitive decline.
- Potential Risks: Mrs. Smith may experience side effects from aducanumab treatment, such as ARIA. These side effects can range from mild headaches to more serious complications such as brain swelling or bleeding. The healthcare team will closely monitor Mrs. Smith for any signs of ARIA and adjust her treatment accordingly.
- Individualized Response: The response to aducanumab treatment can vary significantly from person to person. Some individuals may experience a more significant benefit from the treatment than others. The healthcare team will monitor Mrs. Smith’s progress closely and adjust her treatment plan as needed to optimize her response to the therapy.
Monitoring and Follow-Up
After initiating aducanumab therapy, Mrs. Smith will undergo regular monitoring to assess her response to treatment. This monitoring includes:
- Cognitive Assessments: Regular cognitive assessments will be conducted to track Mrs. Smith’s cognitive function and determine if there are any improvements or changes in her cognitive decline.
- Imaging Studies: Periodic brain imaging studies will be performed to monitor the presence of amyloid plaques and assess the effectiveness of the treatment in reducing their accumulation.
- Safety Monitoring: The healthcare team will closely monitor Mrs. Smith for any signs of ARIA or other side effects associated with aducanumab treatment. They will adjust her treatment plan as needed to minimize the risk of complications.
- Patient and Family Support: Mrs. Smith and her family will receive ongoing support and education about Alzheimer’s disease and aducanumab therapy. The healthcare team will address any concerns or questions they may have and provide guidance on managing the disease and its impact on their lives.
Aducanumab: Impact on the Pharmaceutical Industry
The approval of aducanumab, the first new Alzheimer’s drug in nearly two decades, has sent shockwaves through the pharmaceutical industry. This landmark decision has far-reaching implications, impacting research and development, investment strategies, and the future of Alzheimer’s treatment.
Aducanumab’s Influence on Alzheimer’s Research and Development
Aducanumab’s approval has reignited hope and enthusiasm for Alzheimer’s research. It has demonstrated that targeting amyloid plaques, a hallmark of Alzheimer’s disease, is a viable therapeutic approach. This success is likely to encourage further research into amyloid-targeting therapies, including the development of new antibodies and other innovative approaches. The approval has also sparked renewed interest in other potential Alzheimer’s treatments, such as those targeting tau tangles, another key pathological feature of the disease.
Aducanumab as a Catalyst for Innovation in Neurodegenerative Disease Research
Beyond Alzheimer’s, aducanumab’s success has broader implications for neurodegenerative disease research. It has demonstrated the potential of targeting specific disease-related proteins as a therapeutic strategy. This approach is now being explored for other neurodegenerative conditions, such as Parkinson’s disease, Huntington’s disease, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).
Key Players in the Pharmaceutical Industry Involved in Aducanumab
The development and commercialization of aducanumab involved several key players in the pharmaceutical industry:
- Biogen: The primary developer and manufacturer of aducanumab.
- Eisai: Biogen’s partner in the development and commercialization of aducanumab.
- The Food and Drug Administration (FDA): The regulatory body that approved aducanumab.
- Numerous research institutions and academic centers: Involved in clinical trials and research on aducanumab.
Aducanumab
Aducanumab, an antibody designed to target amyloid plaques in the brain, has sparked significant public debate and media attention. This is due to its potential as a treatment for Alzheimer’s disease, a debilitating neurodegenerative condition with no cure. However, the drug’s journey has been marked by controversy, with varying opinions on its efficacy, cost, and potential risks.
Public Perception of Aducanumab
The public perception of aducanumab has been complex and evolving. Early media coverage often presented the drug as a potential breakthrough, highlighting its ability to reduce amyloid plaques in the brain. However, subsequent discussions have centered on the drug’s effectiveness in slowing cognitive decline, its high cost, and potential side effects.
- Effectiveness: Some studies have shown that aducanumab can slow cognitive decline in some patients with early-stage Alzheimer’s disease. However, other studies have shown less clear results, leading to debates about the drug’s true effectiveness and the specific patient populations that might benefit the most.
- Cost: Aducanumab is a very expensive drug, with an estimated annual cost of over $26,000 per patient. This has raised concerns about access to the drug for all patients who might benefit from it, especially those with limited financial resources.
- Risks: Like all medications, aducanumab carries potential risks, including brain swelling and bleeding. These risks, while generally considered manageable, have contributed to concerns about the drug’s safety profile.
Media Coverage of Aducanumab
The media has played a significant role in shaping public perception of aducanumab. News reports have covered both the potential benefits and risks of the drug, often presenting conflicting viewpoints from researchers, clinicians, and patient advocacy groups.
- Positive Perspectives: Some media reports have highlighted the potential of aducanumab to slow cognitive decline and improve the lives of patients with Alzheimer’s disease. These reports often feature stories of patients who have experienced positive outcomes from using the drug.
- Negative Perspectives: Other media reports have focused on the drug’s high cost, potential risks, and uncertain effectiveness. These reports often cite concerns raised by researchers and patient advocacy groups who question the drug’s true benefits and value.
Role of Public Awareness and Education
Public awareness and education are crucial in shaping a balanced understanding of aducanumab. It is essential for the public to have access to accurate and unbiased information about the drug, including its potential benefits, risks, and limitations.
- Transparency and Open Communication: Pharmaceutical companies, regulatory agencies, and healthcare providers have a responsibility to be transparent about the drug’s development, clinical trials, and potential risks. Open communication can help build trust and facilitate informed decision-making by patients and their families.
- Patient Education and Support: It is crucial to provide patients and their families with comprehensive information about aducanumab, including its potential benefits, risks, and how it might affect their lives. This information should be presented in a clear and understandable manner, allowing patients to make informed decisions about their treatment options.
Aducanumab stands as a testament to the relentless pursuit of scientific breakthroughs in the fight against Alzheimer’s disease. While its role in the treatment landscape remains under active investigation, it has undeniably sparked renewed hope and ignited a wave of research into innovative therapies for this complex condition. The future of aducanumab, with its potential for disease modification and improved patient outcomes, holds immense promise for individuals living with Alzheimer’s and their families, offering a glimmer of optimism in the face of this challenging disease.
Aducanumab is a groundbreaking treatment for Alzheimer’s disease, marking a significant step forward in addressing this debilitating condition. While aducanumab targets amyloid plaques in the brain, other medications like natalizumab , which is used to treat multiple sclerosis, focus on different mechanisms. The development of aducanumab offers hope for a future where Alzheimer’s disease is no longer a terminal diagnosis.