Misoprostol uses extend far beyond its initial role in preventing stomach ulcers, encompassing a wide range of medical applications, from managing postpartum hemorrhage to facilitating medication abortion. This versatile drug has become a cornerstone in various healthcare settings, offering solutions for a diverse array of conditions. Its ability to interact with the body’s natural processes, particularly in the reproductive system, has led to its widespread use and ongoing research, making it a topic of significant interest and debate.
Misoprostol’s versatility is evident in its applications, ranging from its traditional use in treating ulcers to its controversial role in abortion. This article delves into the multifaceted uses of misoprostol, exploring its medical applications, off-label uses, potential side effects, and the ongoing debate surrounding its accessibility and ethical considerations. We will examine the scientific evidence, explore cultural perspectives, and discuss the future implications of this remarkable drug.
Medical Uses of Misoprostol
Misoprostol is a medication primarily used for preventing and treating stomach ulcers and for managing postpartum hemorrhage. It is also used in conjunction with other medications to terminate early pregnancy.
Preventing and Treating Stomach Ulcers
Misoprostol is a synthetic prostaglandin analog that works by protecting the stomach lining from the damaging effects of stomach acid. It achieves this by increasing the production of mucus, which acts as a protective barrier, and by reducing the amount of acid produced by the stomach.
Misoprostol is commonly prescribed to prevent and treat stomach ulcers in patients who are at high risk of developing them, such as those:
- Taking nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), which can damage the stomach lining.
- Having a history of stomach ulcers.
- Suffering from Helicobacter pylori infection, a bacterium that can cause ulcers.
Treating Postpartum Hemorrhage
Postpartum hemorrhage (PPH) is a serious complication of childbirth that occurs when a woman loses a significant amount of blood after delivery. Misoprostol is effective in treating PPH by stimulating the uterus to contract and reduce bleeding.
Misoprostol is administered either orally or vaginally. It is typically used in conjunction with other measures, such as uterine massage and intravenous fluids.
Other Medical Uses
Misoprostol is also used for:
- Induction of labor: Misoprostol can be used to induce labor in women who are at term and whose labor has not started naturally. It works by softening and dilating the cervix.
- Medical abortion: Misoprostol is used in conjunction with mifepristone to terminate early pregnancy. It works by causing the uterus to contract and expel the pregnancy.
Misoprostol for Abortion
Misoprostol, a medication primarily used for treating stomach ulcers, has also become a crucial component in medication abortion. When used in combination with mifepristone, it effectively terminates a pregnancy. Medication abortion, also known as medical abortion, is a safe and effective way to end a pregnancy during the first trimester.
Dosage Regimens and Administration Methods
The dosage and administration of misoprostol for abortion vary depending on the specific regimen being used. Here are some common methods:
- Vaginal administration: This is the most common method. Misoprostol tablets are inserted into the vagina, typically 24-48 hours after taking mifepristone. The dosage usually ranges from 400 to 800 micrograms, depending on the specific regimen.
- Oral administration: In some cases, misoprostol may be taken orally, either in tablet form or dissolved under the tongue. The dosage and timing are similar to vaginal administration.
- Sublingual administration: This method involves placing the misoprostol tablet under the tongue and allowing it to dissolve. It offers faster absorption compared to oral administration.
Potential Side Effects and Risks
Misoprostol can cause side effects, which are generally mild and temporary. The most common side effects include:
- Bleeding: Vaginal bleeding is a common and expected side effect. It can range from light spotting to heavy bleeding, similar to a menstrual period.
- Cramping: Abdominal cramping is another common side effect, which may be mild or severe.
- Nausea and vomiting: Some individuals may experience nausea and vomiting, particularly after oral administration.
- Diarrhea: Diarrhea is a potential side effect, especially when misoprostol is taken orally.
- Fever: A low-grade fever is possible, but a high fever should be reported to a healthcare provider.
In rare cases, misoprostol can cause more serious side effects, such as:
- Incomplete abortion: This occurs when the pregnancy is not fully terminated, requiring further medical intervention.
- Infection: Infection can occur if the uterus is not properly emptied after the abortion.
- Heavy bleeding: Excessive bleeding can lead to anemia and require medical attention.
It’s important to note that misoprostol should only be used under the supervision of a qualified healthcare provider. They can assess individual risks, provide appropriate guidance, and manage any potential complications.
Off-Label Uses of Misoprostol
Misoprostol, originally approved for the treatment of ulcers, has gained popularity for its off-label applications, primarily in obstetrics and gynecology. These uses, not explicitly approved by regulatory agencies, are often driven by clinical experience and research findings, highlighting the drug’s versatility.
Induction of Labor
The ability of misoprostol to soften the cervix and stimulate uterine contractions makes it a potential option for inducing labor. It’s often used when a pregnancy has reached term but labor hasn’t begun naturally.
- Misoprostol can be administered vaginally or orally, depending on the clinical situation and physician preference.
- Studies have shown that misoprostol is effective in inducing labor, with success rates comparable to other methods like oxytocin.
- The drug’s safety profile in this context is generally considered favorable, but potential side effects include uterine hyperstimulation, which can lead to fetal distress, and postpartum hemorrhage.
Cervical Ripening
Misoprostol’s ability to soften the cervix, a process known as cervical ripening, is another off-label use. This is particularly beneficial in cases where the cervix is not yet ready for labor induction or other procedures.
- Cervical ripening with misoprostol is typically performed by inserting the drug vaginally, often in conjunction with other methods like amniotomy (artificial rupture of the amniotic sac).
- Evidence suggests that misoprostol is effective in promoting cervical ripening, leading to a shorter induction time and potentially reducing the need for other interventions.
- However, it’s important to note that misoprostol can also cause uterine contractions, which may be undesirable in some cases.
Ethical Considerations and Risks
While misoprostol’s off-label applications can be beneficial, it’s crucial to consider the ethical and safety implications.
- The use of a drug for unapproved purposes raises concerns about informed consent, as patients may not be fully aware of the potential risks and benefits.
- The lack of standardized guidelines for off-label use can lead to variability in dosing and administration, potentially increasing the risk of adverse effects.
- It’s essential for healthcare professionals to carefully weigh the potential benefits against the risks when considering off-label misoprostol use, ensuring appropriate patient selection and monitoring.
Misoprostol Interactions and Contraindications
Misoprostol, like many other medications, can interact with other drugs and substances, potentially altering its effectiveness or increasing the risk of side effects. It’s also important to be aware of certain medical conditions that may make misoprostol unsafe or inappropriate.
Drug Interactions
Misoprostol can interact with various medications, including:
- Antacids: Antacids containing magnesium or aluminum can reduce the absorption of misoprostol, potentially lessening its effectiveness.
- Antibiotics: Some antibiotics, such as metronidazole, can increase the risk of side effects when taken with misoprostol.
- Blood thinners: Misoprostol can increase the risk of bleeding, especially when taken with blood thinners like warfarin or aspirin.
- Digoxin: Misoprostol can increase the levels of digoxin in the blood, potentially leading to toxicity.
- Diuretics: Misoprostol can increase the risk of dehydration when taken with diuretics.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): Misoprostol can increase the risk of stomach ulcers and bleeding when taken with NSAIDs.
- Oral contraceptives: Misoprostol can reduce the effectiveness of oral contraceptives.
Contraindications
Misoprostol is contraindicated in certain medical conditions, including:
- Active gastrointestinal bleeding: Misoprostol can increase the risk of bleeding, making it unsafe for individuals with active gastrointestinal bleeding.
- Severe liver disease: Misoprostol is primarily metabolized by the liver, and its use in individuals with severe liver disease can lead to an accumulation of the drug, increasing the risk of side effects.
- Severe kidney disease: Misoprostol is excreted by the kidneys, and its use in individuals with severe kidney disease can lead to a buildup of the drug in the body, increasing the risk of toxicity.
- History of ectopic pregnancy: Misoprostol is not effective for treating ectopic pregnancies and can worsen the condition. It is important to note that misoprostol should never be used to attempt to terminate an ectopic pregnancy.
- Known hypersensitivity to misoprostol or prostaglandins: Individuals with known hypersensitivity to misoprostol or prostaglandins should avoid using the medication due to the risk of severe allergic reactions.
Importance of Consulting a Healthcare Professional
It is crucial to consult a healthcare professional before using misoprostol. They can assess your medical history, current medications, and any potential risks associated with using misoprostol. They can also provide guidance on the appropriate dosage and administration method.
Misoprostol Safety and Side Effects
Misoprostol, like any medication, comes with potential side effects. While most are mild and temporary, understanding the risks is crucial for informed decision-making. This section will explore common and serious side effects associated with misoprostol use, offering insights into managing and minimizing potential risks.
Common Side Effects
Common side effects of misoprostol are generally mild and often resolve on their own within a few days. These include:
- Diarrhea: This is a frequent side effect, often occurring within a few hours of taking misoprostol. It can be watery and frequent, but typically subsides within a day or two.
- Cramping: Misoprostol can cause cramping in the abdomen, similar to menstrual cramps. These cramps may be mild or intense and can last for several hours.
- Bleeding: Misoprostol can cause vaginal bleeding, which can range from light spotting to heavy bleeding. The duration and amount of bleeding vary depending on the individual and the reason for taking misoprostol.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Some individuals may experience nausea and vomiting, particularly after taking misoprostol on an empty stomach.
- Headache: Misoprostol can cause headaches in some individuals.
Serious Side Effects
While rare, misoprostol can cause serious side effects. It’s important to be aware of these potential complications and seek immediate medical attention if they occur.
- Uterine Rupture: This is a serious complication that can occur if the uterus is weakened or has been previously damaged. Symptoms may include severe abdominal pain, vaginal bleeding, and fever.
- Infection: Misoprostol can increase the risk of infection, particularly if the medication is used for abortion. Symptoms may include fever, chills, abdominal pain, and foul-smelling vaginal discharge.
- Allergic Reactions: Some individuals may experience allergic reactions to misoprostol, which can range from mild rashes to life-threatening anaphylaxis. Symptoms of an allergic reaction can include hives, itching, swelling, difficulty breathing, and a rapid heartbeat.
Managing and Minimizing Risks, Misoprostol uses
Taking misoprostol as directed by a healthcare professional is crucial for minimizing potential risks. Here are some additional tips for managing and minimizing side effects:
- Take misoprostol with food: Taking misoprostol with food can help reduce nausea and vomiting.
- Stay hydrated: Drinking plenty of fluids can help prevent dehydration, which can worsen diarrhea.
- Use over-the-counter medications: Over-the-counter medications, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help manage cramping and pain.
- Rest: Resting can help your body recover from the effects of misoprostol.
- Contact your healthcare provider: If you experience any unusual or concerning side effects, contact your healthcare provider immediately.
Misoprostol Availability and Access
Misoprostol’s availability and access vary widely across the globe, influenced by legal frameworks, healthcare systems, and cultural norms. While some countries allow unrestricted access, others impose strict regulations or outright bans. Understanding these variations is crucial for ensuring safe and effective use of misoprostol, particularly for medical abortion.
Regulations and Restrictions
The legal status of misoprostol for medical abortion differs significantly across countries. In some regions, like the United States, misoprostol is available by prescription for medical abortion. However, in other countries, like many in Latin America and Africa, it may be strictly controlled or prohibited for this purpose.
- United States: Misoprostol is available by prescription for medical abortion, and in some states, it can be accessed via telehealth platforms.
- Canada: Misoprostol is available by prescription for medical abortion and is covered by provincial healthcare plans.
- United Kingdom: Misoprostol is available by prescription for medical abortion, and women can access it through the National Health Service (NHS).
- India: Misoprostol is available by prescription for medical abortion, but access can be limited due to stigma and lack of awareness.
- Latin America: Misoprostol access for medical abortion varies widely. Some countries, like Argentina and Uruguay, have legalized abortion and have relatively easier access to misoprostol, while others, like El Salvador and Nicaragua, have strict bans on abortion and misoprostol access is highly restricted.
Role of Healthcare Providers
Healthcare providers play a crucial role in ensuring safe and effective access to misoprostol.
- Prescribing and Dispensing: Healthcare providers, such as physicians and nurses, are responsible for prescribing and dispensing misoprostol. They assess patients’ medical history, provide counseling on potential risks and benefits, and ensure appropriate dosage and administration.
- Providing Information and Support: Healthcare providers should provide comprehensive information about misoprostol, including its potential side effects and contraindications. They should also offer emotional support and answer any questions patients may have.
- Managing Complications: Healthcare providers must be equipped to manage potential complications associated with misoprostol use, such as bleeding, pain, or incomplete abortion. They should have access to appropriate resources and emergency care facilities.
Challenges and Barriers to Access
Despite its availability in many countries, accessing misoprostol can be challenging, particularly in low-resource settings.
- Legal Restrictions: Strict laws and regulations surrounding abortion can significantly hinder access to misoprostol. In some countries, even possession of misoprostol can be criminalized.
- Limited Healthcare Infrastructure: In low-resource settings, access to qualified healthcare providers and facilities may be limited, making it difficult for women to obtain misoprostol safely and effectively.
- Stigma and Lack of Awareness: Stigma surrounding abortion and misoprostol can prevent women from seeking information and accessing services. Lack of awareness about misoprostol’s safety and effectiveness can also contribute to limited access.
- Financial Barriers: The cost of misoprostol and related healthcare services can be a significant barrier for women, particularly in low-income countries. This can prevent them from seeking medical abortion or accessing appropriate care.
Misoprostol Research and Development: Misoprostol Uses
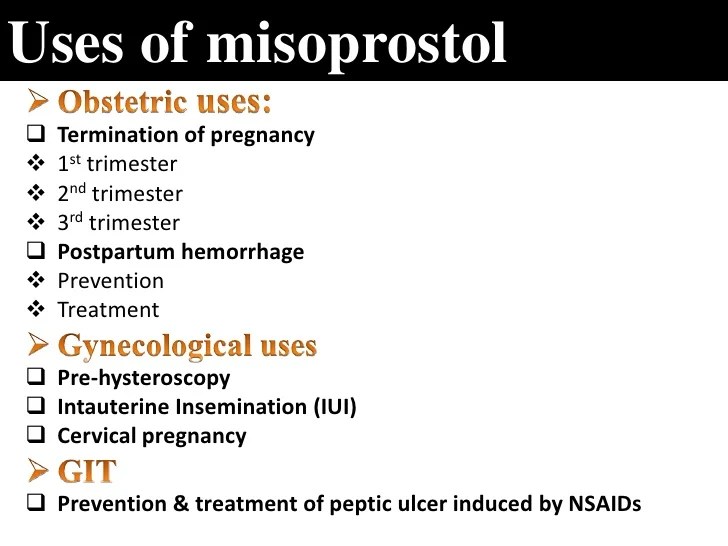
Misoprostol, a synthetic prostaglandin analogue, has been extensively studied and used in various medical fields for decades. Ongoing research continues to explore its potential for new applications and improvements in its formulation, leading to advancements in its effectiveness and safety.
New Uses and Applications
Researchers are actively investigating new uses for misoprostol beyond its established applications in treating peptic ulcers, inducing labor, and facilitating medical abortion. For example, studies are exploring its potential in treating conditions like:
- Cervical ripening: Misoprostol has shown promise in preparing the cervix for labor induction, potentially reducing the need for other interventions.
- Gastrointestinal disorders: Studies are exploring misoprostol’s potential in treating conditions like inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), as well as its role in preventing gastric ulcers caused by non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
- Cancer treatment: Some research suggests that misoprostol might have anti-cancer properties, potentially enhancing the effectiveness of certain chemotherapy regimens.
- Other conditions: Researchers are investigating misoprostol’s potential in treating a range of other conditions, including postpartum hemorrhage, endometriosis, and certain types of infertility.
Improved Formulations
Efforts are underway to improve the formulation of misoprostol, aiming to enhance its effectiveness, reduce side effects, and improve patient compliance. Some of the areas of focus include:
- Extended-release formulations: Researchers are developing extended-release formulations of misoprostol to provide sustained therapeutic effects, reducing the need for frequent dosing.
- Improved bioavailability: Studies are investigating ways to enhance the absorption and bioavailability of misoprostol, leading to more effective treatment.
- Targeted delivery systems: Researchers are exploring targeted delivery systems to deliver misoprostol directly to the site of action, minimizing systemic side effects.
Future Prospects
Misoprostol’s versatility and ongoing research make it a promising drug with significant potential for the future. The development of new uses and improved formulations could lead to:
- Improved treatment options: Misoprostol could offer new and effective treatment options for a wide range of medical conditions.
- Enhanced patient outcomes: Improved formulations and targeted delivery systems could enhance the effectiveness of misoprostol while minimizing side effects, leading to better patient outcomes.
- Cost-effectiveness: Misoprostol’s low cost and wide availability make it an attractive option for treating various conditions, potentially reducing healthcare costs.
Emerging Concerns and Controversies
Despite its potential benefits, misoprostol’s use is not without controversy. Some emerging concerns include:
- Safety in pregnancy: Misoprostol’s use in early pregnancy for medical abortion raises concerns about potential risks, especially in cases of ectopic pregnancy or undiagnosed uterine anomalies.
- Off-label use: The increasing use of misoprostol for off-label purposes, such as treating postpartum hemorrhage, raises concerns about the lack of sufficient clinical evidence to support its efficacy and safety in these settings.
- Access and availability: Misoprostol’s availability and access vary significantly across different regions, raising concerns about equitable access to this essential medication.
- Potential for misuse: Misoprostol’s availability online and its use in medical abortion raise concerns about potential misuse and abuse.
Misoprostol in Different Cultures and Societies
Misoprostol’s use varies significantly across cultures and societies, influenced by factors like religious beliefs, legal frameworks, and access to healthcare. Understanding these differences is crucial for promoting responsible and safe use of the medication.
Cultural and Religious Influences
Cultural and religious beliefs significantly impact the acceptability and use of misoprostol, particularly for abortion.
- In some cultures, abortion is strictly prohibited, and misoprostol use for this purpose is considered unethical and illegal.
- In other cultures, abortion is more readily accepted, and misoprostol may be used as a safe and effective method of terminating unwanted pregnancies.
- Religious beliefs also play a role, with some religions opposing abortion in all circumstances, while others allow it under specific conditions.
For example, in countries with strong Catholic influences, abortion is generally frowned upon, and misoprostol use for this purpose is often considered morally wrong. Conversely, in countries with more secular populations, abortion is more widely accepted, and misoprostol may be used more readily.
Ethical and Legal Implications
The ethical and legal implications of misoprostol use are complex and vary across jurisdictions.
- In some countries, misoprostol is readily available for medical use, including abortion, while in others, it is tightly controlled or even banned.
- The legal status of abortion also influences misoprostol’s use, with some countries permitting abortion on demand, while others restrict it to specific circumstances.
- Ethical concerns surrounding misoprostol use include the potential for misuse, the safety of self-administered medication, and the right to access safe and legal abortion services.
For instance, in the United States, access to abortion is highly contested, and misoprostol use for this purpose is subject to legal restrictions and ethical debates. In contrast, in some European countries, abortion is legal and accessible, and misoprostol is widely used for this purpose.
Public Awareness and Education
Public awareness and education play a critical role in promoting safe and responsible use of misoprostol.
- Accurate information about misoprostol’s uses, risks, and benefits is crucial for informed decision-making.
- Public health campaigns can educate individuals about safe and effective ways to use misoprostol, particularly for abortion.
- Access to reliable sources of information, such as healthcare providers and reputable online resources, can help individuals make informed choices about misoprostol use.
For example, in countries where misoprostol is used for abortion, public health campaigns can provide information about the proper dosage, administration, and potential side effects. This can help ensure that individuals use the medication safely and effectively.
Misoprostol and Women’s Health
Misoprostol has significantly impacted women’s health, offering both potential benefits and risks. Its accessibility and effectiveness in managing various gynecological conditions, including menstrual disorders and postpartum hemorrhage, have been widely recognized. However, its use for abortion has sparked ethical and legal debates, highlighting the need for informed decision-making and safe access to reproductive healthcare services.
Empowering Women with Information
Providing women with comprehensive information about misoprostol and their reproductive rights is crucial. This includes understanding its various uses, potential risks, and alternative options. Educating women about their legal and medical rights empowers them to make informed decisions about their bodies and reproductive health.
Advocating for Safe and Effective Abortion Care
Misoprostol’s use in medical abortion, particularly in regions with limited access to safe and legal abortion services, has been a subject of ongoing debate. Advocates for reproductive rights argue that access to safe and effective abortion care, including the use of misoprostol, is essential for women’s health and well-being. They emphasize the importance of ensuring that women have access to accurate information, qualified healthcare providers, and safe environments for accessing abortion services.
Misoprostol and the Future of Healthcare
Misoprostol, a medication initially developed for the treatment of ulcers, has become a pivotal player in healthcare with its diverse applications. Its use extends beyond its initial purpose, encompassing areas like abortion, labor induction, and even potential treatment for certain cancers. As medical technology continues to evolve and societal norms shift, misoprostol’s role in healthcare is poised to become even more significant.
The Future of Misoprostol in Healthcare
The future of misoprostol in healthcare is likely to be characterized by a convergence of advancements in medical technology, evolving societal norms, and a deeper understanding of its pharmacological properties. This confluence of factors suggests a future where misoprostol plays a more prominent and multifaceted role in addressing various healthcare needs.
Potential New Applications of Misoprostol
Misoprostol’s potential applications are not limited to its current uses. Research and development are ongoing, exploring new avenues for utilizing its pharmacological properties.
New Applications
- Cancer Treatment: Studies suggest that misoprostol may hold promise as a treatment for certain types of cancer, particularly those affecting the gastrointestinal tract. Its ability to inhibit cell growth and induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) makes it a potential therapeutic agent for cancer treatment.
- Wound Healing: Misoprostol’s ability to stimulate prostaglandin production has led to research exploring its potential role in promoting wound healing. Studies suggest that it may accelerate the healing process in various types of wounds, including burns and ulcers.
- Neurological Disorders: Research is investigating misoprostol’s potential therapeutic applications in neurological disorders, such as Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease. Its ability to modulate neurotransmitter activity and protect neurons from damage suggests potential benefits in these conditions.
Ethical and Societal Implications
The expansion of misoprostol’s applications raises ethical and societal concerns.
Ethical Considerations
- Access and Equity: As misoprostol becomes more widely used, ensuring equitable access to this medication becomes crucial. Addressing disparities in access based on socioeconomic status, geographical location, and other factors is essential.
- Informed Consent: Patients must be provided with comprehensive information about the potential risks and benefits of misoprostol use, allowing them to make informed decisions about their treatment.
- Regulation and Oversight: Effective regulation and oversight are essential to ensure the safe and ethical use of misoprostol. This includes establishing clear guidelines for its prescription, distribution, and use in different clinical settings.
Societal Implications
- Reproductive Rights: The use of misoprostol for abortion raises complex societal issues related to reproductive rights. Ensuring access to safe and legal abortion services is crucial, and misoprostol’s role in this context needs careful consideration.
- Public Perception: Public perception of misoprostol can be influenced by its association with abortion. Addressing misconceptions and promoting accurate information about its various uses is important to ensure a balanced understanding of this medication.
- Social Norms: The widespread use of misoprostol may challenge traditional social norms surrounding healthcare and reproductive choices. This presents an opportunity for open dialogue and societal adaptation to embrace new possibilities in healthcare.
Misoprostol, with its diverse applications and ongoing research, stands as a testament to the evolving landscape of medicine. Understanding its uses, potential benefits, and associated risks is crucial for both healthcare professionals and individuals seeking information about this powerful drug. As we move forward, continued research and open dialogue are essential for ensuring the safe and responsible use of misoprostol, ultimately benefiting patients and advancing the field of medicine.
Misoprostol is a medication with a range of uses, including inducing labor and treating stomach ulcers. While it’s a versatile drug, it’s important to remember that medications like glivec , used to treat certain types of cancer, have entirely different mechanisms and applications. Misoprostol’s effectiveness is also dependent on factors like dosage and individual patient needs, making it crucial to consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice.