Suboxone side effects set the stage for this exploration, offering readers a comprehensive understanding of the potential benefits and risks associated with this medication. Suboxone, a combination of buprenorphine and naloxone, is a medication used to treat opioid addiction. While it can be effective in helping individuals overcome addiction, it’s crucial to be aware of the possible side effects that may accompany its use.
This article will delve into the common and serious side effects of Suboxone, examining their potential impact on individuals’ health and well-being. We’ll also discuss interactions with other medications, the potential for dependence and withdrawal, and the long-term effects of Suboxone use. Additionally, we’ll address important considerations for pregnant and breastfeeding women, as well as individuals who drive or consume alcohol. By providing a thorough understanding of Suboxone’s potential side effects, this information aims to empower individuals to make informed decisions about their treatment and overall health.
Introduction to Suboxone
Suboxone is a medication used to treat opioid addiction. It contains two medications: buprenorphine and naloxone.
Buprenorphine is a partial opioid agonist, meaning it binds to opioid receptors in the brain but produces a weaker effect than full opioid agonists like heroin or morphine. Naloxone is an opioid antagonist, meaning it blocks the effects of opioids.
Suboxone is used to help people who are addicted to opioids to reduce their cravings, withdraw safely, and prevent relapse.
Mechanism of Action
Buprenorphine and naloxone work together to help people overcome opioid addiction.
Buprenorphine binds to opioid receptors in the brain, reducing cravings and withdrawal symptoms. Because it is a partial agonist, it does not produce the same euphoric effects as full opioid agonists. This helps to prevent relapse by reducing the rewarding effects of opioids.
Naloxone is included in Suboxone to prevent misuse and abuse. If Suboxone is injected, naloxone blocks the effects of buprenorphine, preventing the user from getting high.
Use in Opioid Addiction Treatment
Suboxone is a valuable tool for treating opioid addiction. It can help people:
- Reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms
- Prevent relapse
- Improve overall health and well-being
Suboxone is typically prescribed as part of a comprehensive treatment plan that includes counseling and behavioral therapy.
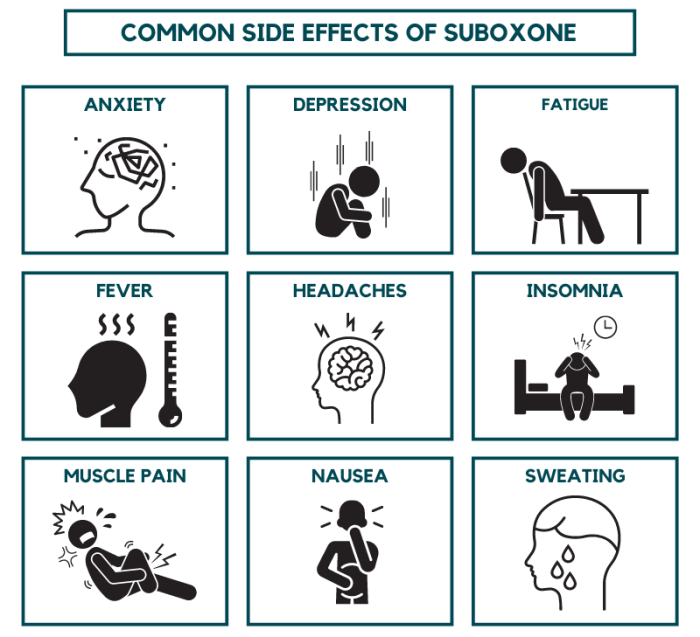
Common Side Effects

Suboxone, a medication used to treat opioid addiction, can cause a range of side effects. These side effects are generally mild and temporary, but some can be more severe and may require medical attention. Understanding the potential side effects of Suboxone is crucial for patients to manage their treatment effectively.
Gastrointestinal Side Effects
Gastrointestinal side effects are among the most common experienced by Suboxone users. These side effects can range from mild discomfort to more severe complications.
- Constipation: This is a very common side effect of Suboxone. It occurs because buprenorphine, the active ingredient in Suboxone, slows down the movement of food through the digestive system. Patients should increase their intake of fiber and fluids to help prevent constipation.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Some patients experience nausea and vomiting, especially during the initial stages of Suboxone treatment. This is often due to the medication’s effects on the central nervous system. Over-the-counter medications, such as anti-nausea drugs, can help manage these symptoms.
- Dry Mouth: Buprenorphine can reduce saliva production, leading to a dry mouth. Patients can address this by drinking plenty of water and using sugar-free gum or lozenges.
- Abdominal Pain: Some patients experience abdominal pain or discomfort. This is often associated with constipation, but other factors may contribute to this side effect.
Neurological Side Effects
Suboxone can also affect the central nervous system, leading to various neurological side effects.
- Dizziness: Dizziness is a common side effect, particularly during the initial stages of treatment. Patients should avoid activities that require alertness, such as driving, until they understand how Suboxone affects them.
- Headaches: Headaches are another common neurological side effect. Over-the-counter pain relievers can usually manage these headaches.
- Sleep Disturbances: Some patients experience difficulty sleeping or insomnia, particularly during the initial stages of treatment. Patients should maintain a regular sleep schedule and avoid caffeine and alcohol before bedtime.
- Fatigue: Fatigue is a common side effect of Suboxone, which can affect a patient’s energy levels and ability to perform daily tasks. Patients should prioritize rest and sleep to manage fatigue.
Psychological Side Effects
Suboxone can also affect mood and mental state, leading to psychological side effects.
- Mood Swings: Some patients experience mood swings, including irritability, anxiety, and depression. These mood swings can be exacerbated by stress or other factors.
- Insomnia: Insomnia is a common side effect of Suboxone, which can affect a patient’s sleep patterns and quality of sleep.
- Cognitive Impairment: Some patients experience cognitive impairment, including difficulty concentrating or remembering things. This side effect is usually temporary and improves as the body adjusts to the medication.
Other Side Effects, Suboxone side effects
In addition to the common side effects listed above, Suboxone can also cause other less frequent side effects.
- Sweating: Some patients experience increased sweating, particularly during the initial stages of treatment.
- Muscle Aches: Muscle aches are another less common side effect. Patients should consult with their doctor if these aches are severe or persistent.
- Skin Reactions: Some patients experience skin reactions, such as itching or rash. These reactions are usually mild and resolve on their own, but patients should consult with their doctor if they are severe or persistent.
- Allergic Reactions: While rare, some patients may experience allergic reactions to Suboxone. Symptoms of an allergic reaction can include hives, swelling, difficulty breathing, or a rapid heartbeat. Patients should seek immediate medical attention if they experience an allergic reaction.
Serious Side Effects
While Suboxone is generally considered safe, it can cause serious side effects, some of which can be life-threatening. It’s important to be aware of these potential risks and seek immediate medical attention if you experience any severe reactions.
Serious Side Effects of Suboxone
Serious side effects of Suboxone are rare, but they can occur. Some of the most serious side effects include:
- Heart problems: Suboxone can increase your risk of heart problems, including heart attack, stroke, and irregular heartbeat. This risk is higher if you have a history of heart disease or other risk factors.
- Respiratory depression: Suboxone can slow down your breathing, which can be dangerous, especially if you have a history of breathing problems.
- Seizures: Suboxone can increase your risk of seizures, especially if you have a history of seizures or are withdrawing from other opioids.
- Liver problems: Suboxone can cause liver damage, especially if you have a history of liver disease or drink alcohol excessively.
- Allergic reactions: Some people may have allergic reactions to Suboxone, which can be life-threatening. Symptoms of an allergic reaction include rash, itching, swelling, difficulty breathing, and dizziness.
Risks Associated with Serious Side Effects
The risks associated with serious side effects of Suboxone depend on several factors, including your overall health, medical history, and how you use the medication. Here are some of the key risks:
- Dosage: Taking a higher dose of Suboxone than prescribed increases your risk of serious side effects.
- Drug interactions: Suboxone can interact with other medications, including over-the-counter drugs, and increase the risk of serious side effects.
- Pre-existing conditions: If you have pre-existing health conditions, such as heart disease, liver disease, or a history of seizures, you may be at increased risk of serious side effects from Suboxone.
- Alcohol consumption: Mixing Suboxone with alcohol can increase your risk of serious side effects, including respiratory depression.
Seeking Immediate Medical Attention
If you experience any of the following symptoms after taking Suboxone, seek immediate medical attention:
- Chest pain or tightness
- Shortness of breath
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat
- Seizures
- Yellowing of the skin or eyes
- Severe rash, itching, or swelling
- Difficulty breathing
- Dizziness
- Loss of consciousness
Interactions with Other Medications
Suboxone can interact with various medications, potentially altering their effectiveness or increasing the risk of side effects. Understanding these interactions is crucial for ensuring safe and effective treatment.
It is essential to inform your doctor about all medications you are taking, including over-the-counter drugs, herbal supplements, and vitamins. This information allows your doctor to assess potential interactions and make appropriate adjustments to your treatment plan.
Suboxone, a medication used to treat opioid addiction, can have a variety of side effects, including nausea, constipation, and withdrawal symptoms. While these are common, it’s important to be aware of less frequent but potentially serious side effects. For example, Suboxone can interact with certain medications, including cardiac glycosides , which are used to treat heart conditions. If you are taking Suboxone, it’s crucial to discuss any other medications you’re on with your doctor to ensure safe and effective treatment.
Medications That Can Interact with Suboxone
Suboxone can interact with various medications, including:
- Opioids: Suboxone can interact with other opioids, such as heroin, morphine, or oxycodone, increasing the risk of overdose. This is because Suboxone contains buprenorphine, a partial opioid agonist, which can block the effects of other opioids.
- Benzodiazepines: Benzodiazepines, such as Xanax, Valium, and Ativan, can increase the sedative effects of Suboxone, leading to drowsiness, dizziness, and difficulty breathing.
- Antidepressants: Some antidepressants, such as SSRIs (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors) and SNRIs (serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors), can interact with Suboxone, increasing the risk of serotonin syndrome, a potentially life-threatening condition.
- Antipsychotics: Antipsychotics, such as Risperdal, Zyprexa, and Seroquel, can interact with Suboxone, increasing the risk of sedation, dizziness, and confusion.
- Antibiotics: Certain antibiotics, such as erythromycin and clarithromycin, can inhibit the metabolism of buprenorphine, increasing its levels in the body and potentially leading to side effects.
- Antifungal medications: Antifungal medications, such as ketoconazole and itraconazole, can interact with Suboxone, increasing the risk of side effects.
Consequences of Drug Interactions
Drug interactions can have various consequences, including:
- Increased risk of side effects: Interactions can lead to an increase in the severity or frequency of side effects, such as drowsiness, dizziness, nausea, and vomiting.
- Reduced effectiveness of medications: Interactions can decrease the effectiveness of medications, making them less effective in treating the intended condition.
- Increased risk of overdose: Interactions can increase the risk of overdose, especially when Suboxone is combined with other opioids or sedatives.
- Serotonin syndrome: Interactions with certain antidepressants can lead to serotonin syndrome, a potentially life-threatening condition characterized by confusion, agitation, fever, and muscle rigidity.
Dependence and Withdrawal
While Suboxone is designed to help people overcome opioid addiction, it can also be habit-forming. Understanding the potential for dependence and withdrawal symptoms is crucial for successful treatment.
Suboxone Dependence
Suboxone contains buprenorphine, a partial opioid agonist. This means that it activates the opioid receptors in the brain, but to a lesser extent than full opioid agonists like heroin or morphine. While Suboxone can reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms, it can also lead to dependence. This means that your body can become accustomed to the presence of buprenorphine, and you may experience withdrawal symptoms if you stop taking it abruptly.
Suboxone and Pregnancy
Using Suboxone during pregnancy is a complex issue that requires careful consideration of both the risks and benefits. While Suboxone can help manage opioid addiction, it can also have potential effects on the developing fetus. It’s crucial to discuss the risks and benefits with your doctor to make an informed decision about the best course of treatment.
Risks of Suboxone Use During Pregnancy
The use of Suboxone during pregnancy can pose certain risks to the developing fetus. These risks are important to understand and discuss with your doctor.
- Neonatal Opioid Withdrawal Syndrome (NOWS): This occurs when a baby is born dependent on opioids and experiences withdrawal symptoms after birth. Symptoms can include irritability, tremors, high-pitched crying, and difficulty feeding. While Suboxone is less likely to cause severe NOWS compared to other opioids, it can still happen.
- Birth Defects: Some studies suggest a possible association between Suboxone use during pregnancy and certain birth defects, although more research is needed to confirm this link.
- Premature Birth: There is a potential risk of premature birth associated with Suboxone use during pregnancy.
- Low Birth Weight: Babies born to mothers who use Suboxone during pregnancy may have a lower birth weight than expected.
Benefits of Suboxone Use During Pregnancy
Despite the potential risks, there are also benefits to consider when using Suboxone during pregnancy.
- Reduced Risk of Opioid Overdose: Suboxone can help prevent opioid overdose, which is a significant risk for pregnant women with opioid addiction.
- Improved Maternal Health: Suboxone can help improve the overall health of the pregnant mother by reducing cravings and withdrawal symptoms, allowing for better nutrition and prenatal care.
- Reduced Risk of Fetal Exposure to Other Drugs: Suboxone can help reduce the risk of the fetus being exposed to other illicit drugs, which can have more severe consequences for the developing baby.
Managing Suboxone Use During Pregnancy
If you are pregnant and considering using Suboxone, it is essential to work closely with your doctor and a qualified addiction specialist. They can help you:
- Assess your individual risks and benefits: Your doctor will consider your medical history, addiction history, and pregnancy status to determine if Suboxone is the right treatment for you.
- Monitor your pregnancy closely: Regular prenatal care is crucial to monitor the health of both you and your baby.
- Manage any potential side effects: Your doctor can help manage any side effects you may experience from Suboxone.
- Develop a plan for postpartum care: It’s important to have a plan in place for managing your addiction and caring for your baby after delivery.
Suboxone and Breastfeeding
Suboxone can be passed into breast milk, and it’s important to discuss the risks and benefits with your doctor. While Suboxone is generally considered safe for breastfeeding, there is a risk of the baby experiencing withdrawal symptoms. Your doctor can help you make the best decision for you and your baby.
Suboxone and Breastfeeding
Suboxone, a medication used to treat opioid addiction, can be a safe and effective treatment option for breastfeeding mothers. However, it’s crucial to weigh the potential risks and benefits of using Suboxone while breastfeeding. This decision should be made in consultation with a healthcare professional who can provide personalized guidance based on the individual’s circumstances.
Transfer of Suboxone to Breast Milk
Suboxone, which contains buprenorphine and naloxone, can be transferred to breast milk. The amount of Suboxone that passes into breast milk is relatively low, and most of it is inactive due to the naloxone component. However, the buprenorphine that does transfer can potentially affect the infant.
Risks and Benefits of Suboxone Use During Breastfeeding
- Potential Risks for the Infant:
- Sedation: Suboxone can cause sedation in infants, potentially affecting their breathing, feeding, and development.
- Withdrawal Symptoms: Infants exposed to Suboxone in breast milk may experience withdrawal symptoms after breastfeeding is stopped.
- Long-Term Effects: The long-term effects of Suboxone exposure in breast milk are not fully understood.
- Benefits for the Mother:
- Improved Physical and Mental Health: Suboxone can help mothers manage opioid cravings and withdrawal symptoms, leading to improved physical and mental health.
- Stable Environment for the Infant: A mother’s recovery from opioid addiction can create a more stable and nurturing environment for the infant.
Managing Suboxone Use During Breastfeeding
- Monitor the Infant: It’s crucial to monitor the infant for any signs of sedation or withdrawal symptoms.
- Breastfeed at the Lowest Possible Dose: Healthcare providers may recommend adjusting the Suboxone dose to the lowest effective level to minimize the amount transferred to breast milk.
- Pump and Dump: In some cases, healthcare providers may recommend pumping and discarding breast milk for a period of time to reduce the amount of Suboxone in the milk.
- Consult with a Lactation Consultant: A lactation consultant can provide support and guidance on breastfeeding techniques and strategies to maximize milk production and infant feeding.
Suboxone and Driving
Suboxone, like many medications, can potentially affect your ability to drive safely. It’s crucial to understand the potential impact of Suboxone on your driving skills and take necessary precautions to ensure your safety and the safety of others on the road.
Potential Impact of Suboxone on Driving
Suboxone can cause side effects that might impair your driving abilities. These side effects can include:
- Drowsiness
- Dizziness
- Confusion
- Slowed reaction time
These side effects can make it difficult to concentrate, react quickly to changing road conditions, and maintain control of your vehicle.
Risks Associated with Driving While Taking Suboxone
Driving under the influence of Suboxone can increase the risk of accidents. This is because the medication can:
- Impair your judgment and decision-making abilities.
- Reduce your awareness of your surroundings.
- Slow your reflexes and reaction time.
These factors can lead to a higher risk of collisions, especially in situations requiring quick responses, such as merging, changing lanes, or reacting to sudden hazards.
Recommendations for Safe Driving Practices While on Suboxone
If you are taking Suboxone, it is essential to prioritize safety and follow these recommendations:
- Avoid driving if you experience drowsiness, dizziness, or other side effects that could impair your driving ability.
- Start with short trips and gradually increase your driving time as you adjust to the medication.
- Avoid driving at night or in challenging weather conditions.
- Take breaks frequently to avoid fatigue.
- Avoid driving after consuming alcohol or other substances that can interact with Suboxone.
- Consult your doctor about any concerns you have regarding driving while on Suboxone.
It’s crucial to be aware of the potential risks associated with driving while taking Suboxone and to take necessary precautions to ensure your safety and the safety of others on the road.
Suboxone and Alcohol
Combining Suboxone with alcohol can be dangerous and potentially life-threatening. Both substances depress the central nervous system, and when taken together, they can have additive effects, leading to severe consequences.
Increased Risk of Adverse Effects
Consuming alcohol while taking Suboxone can increase the risk of experiencing adverse effects, including:
- Respiratory depression: This occurs when breathing slows down or stops altogether. It can be fatal, especially when alcohol is involved.
- Overdose: Combining Suboxone with alcohol can increase the risk of an overdose, as both substances can suppress the central nervous system. Symptoms of an overdose may include drowsiness, confusion, slow breathing, and loss of consciousness.
- Drowsiness and sedation: Both Suboxone and alcohol can cause drowsiness and sedation, making it dangerous to drive or operate machinery.
- Impaired judgment and coordination: Alcohol can impair judgment and coordination, making it difficult to make safe decisions and perform tasks that require physical dexterity.
- Increased risk of falls and injuries: Alcohol can increase the risk of falls and injuries, especially in individuals taking Suboxone, as the medication can also cause dizziness and lightheadedness.
Guidance on Avoiding Alcohol Consumption
It is strongly recommended to avoid alcohol consumption entirely while taking Suboxone. If you are struggling with alcohol dependence, it is important to seek professional help to address this issue.
Suboxone and Other Substances: Suboxone Side Effects
Combining Suboxone with other substances can be extremely dangerous and potentially life-threatening. This is because Suboxone interacts with various medications and substances, leading to unpredictable and harmful effects.
Potential Risks of Combining Suboxone with Other Substances
It’s crucial to avoid using any other substances while taking Suboxone. Mixing Suboxone with other drugs can increase the risk of:
- Overdose: Combining Suboxone with opioids, benzodiazepines, or alcohol can lead to severe respiratory depression, coma, and even death.
- Increased Side Effects: Mixing Suboxone with other substances can amplify its side effects, making them more intense and unpleasant.
- Drug Interactions: Suboxone can interact with numerous medications, leading to unexpected and dangerous consequences.
- Treatment Failure: Using other substances can interfere with the effectiveness of Suboxone, hindering your recovery from opioid addiction.
Examples of Substances that Can Interact with Suboxone
- Opioids: Combining Suboxone with other opioids, such as heroin, morphine, or oxycodone, can lead to a dangerous buildup of opioids in the body, increasing the risk of overdose.
- Benzodiazepines: Mixing Suboxone with benzodiazepines, such as Xanax, Valium, or Klonopin, can significantly increase the risk of respiratory depression, coma, and death.
- Alcohol: Combining Suboxone with alcohol can amplify the effects of both substances, increasing the risk of respiratory depression, sedation, and impaired judgment.
- Certain Medications: Suboxone can interact with various medications, including antidepressants, anti-anxiety medications, and anti-seizure medications. Always inform your doctor about all medications you are taking, including over-the-counter drugs and herbal supplements.
Importance of Avoiding Substance Use While Taking Suboxone
- Your safety is paramount. Combining Suboxone with other substances can have serious, even fatal, consequences.
- Suboxone is designed to help you overcome opioid addiction. Using other substances can undermine your treatment goals and hinder your recovery.
- Open communication with your doctor is crucial. Inform them about any substances you are using or considering using, as they can advise you on safe and effective treatment options.
Understanding the potential side effects of Suboxone is essential for individuals undergoing treatment for opioid addiction. While this medication can be a valuable tool in recovery, it’s crucial to be aware of its potential risks. By working closely with healthcare professionals, individuals can effectively manage any side effects and maximize the benefits of Suboxone therapy. Remember, open communication with your doctor is key to ensuring a safe and successful treatment journey.